The following procedures are commonly involved in the automated assembly of plastic emulsion pumps.
Silo supply is the transfer of individual plastic components from a silo to a conveyor belt, such as a pump body, pump cover, piston, da sauransu. A vibratory tray can be used to automate this process. This can be automated using vibratory discs, feeding robots, and other devices.

Assembly Station – On the conveyor belt, components such as pump bodies, pump covers, laima, and so on enter the automatic assembly station. The assembly station performs positioning and assembly using manipulators, assembly fixtures, and other tools. The assembly procedure can be carried out by manipulators picking up individual components for assembly or by components being automatically conveyed to the assembly station by the conveyor.

Inspection Station – The assembled pump enters the inspection station, where sensors and inspection equipment inspect the assembly’s quality. Sensors inspect the assembly’s quality, such as the fit of the pump body to the pump cover, the sealing of the piston to the pump body, da sauransu.

Pumps that pass the quality inspection are automatically marked with a serial number and then transferred to the automatic packing station for packaging. Pumps that are not qualified will be marked as defective and removed.
Finished Product Output – Finished packaged products that are ready for storage or shipment are automatically output via conveyor belt.
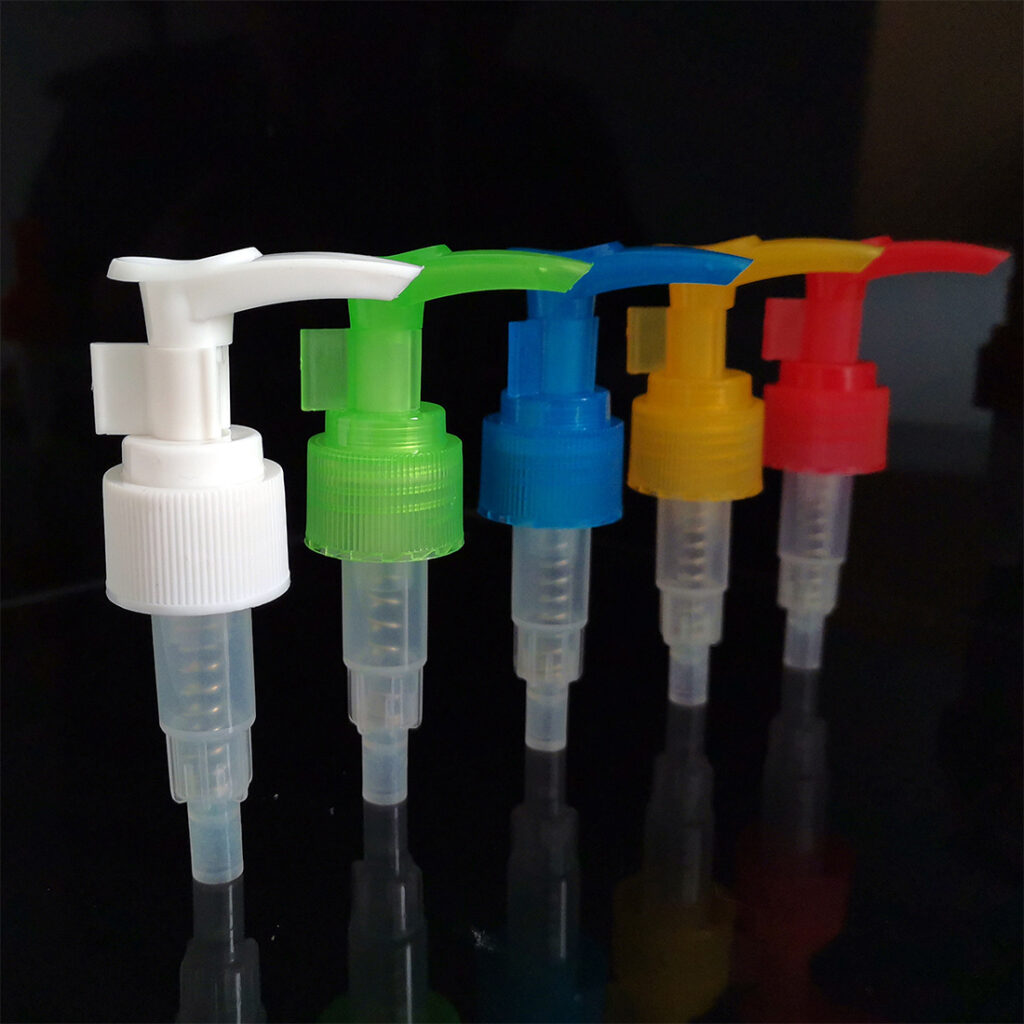

Dukkanin tsarin haɗuwa ta atomatik ta amfani da mutum-mutumi, na'urori masu auna firikwensin, da shirin PLC don cim ma aiki ta atomatik da sarrafa inganci ba tare da buƙatar sa hannun ɗan adam ba, da yawa inganta taro yadda ya dace. Don kula da m aiki na atomatik taro tsari, dole ne mu yi la'akari da tsarin ciyarwa ta atomatik, kiyaye kayan aiki, ingancin feedback, da sauran taimako.