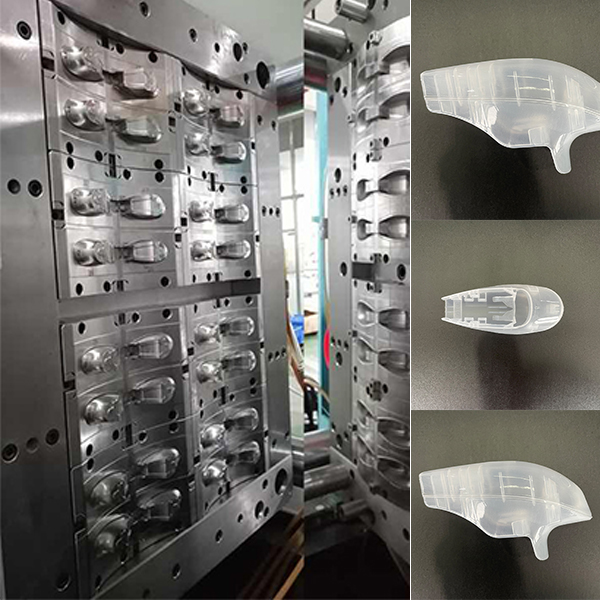
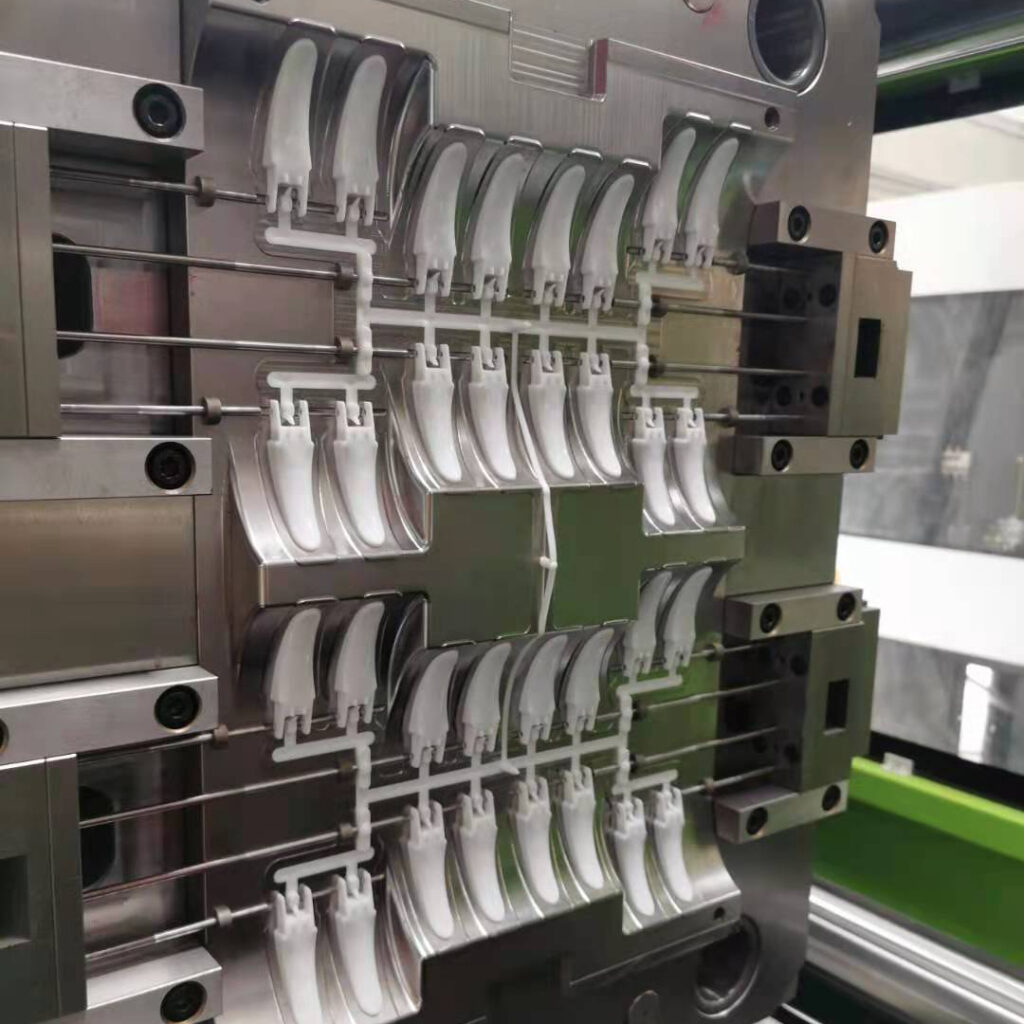
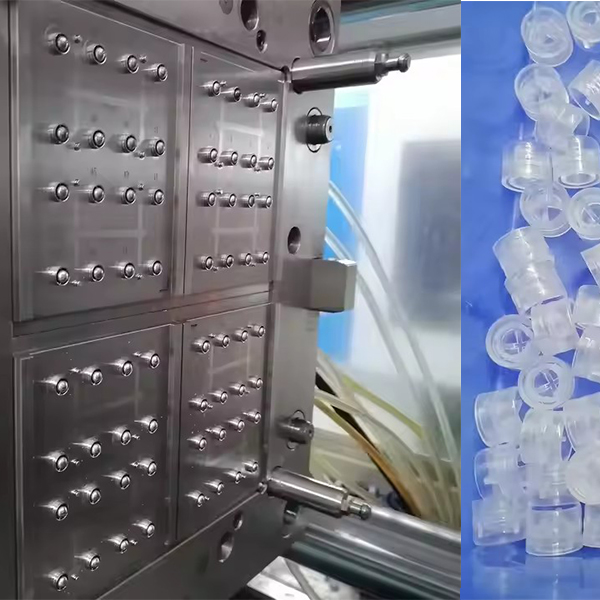
Definicja pleśni
Forma jest wyspecjalizowanym narzędziem do tworzenia części produktów i jest głównym sprzętem procesowym w produkcji przemysłowej.
Według słownika mechanicznych procesów produkcyjnych, Forma to urządzenie, które kontroluje kształt i rozmiar obiektu produkcyjnego.
Formy są używane z urządzeniami do formowania części metalowych, takich jak tłoczenie, kucie, wyrzucenie, i casting, lub ze sprzętem do formowania części niemetalicznych, takich jak tworzywa sztuczne, guma, i ceramika. Mogą stworzyć szeroką gamę części metalowych i niemetalicznych. Stała się ważną metodą przetwarzania we współczesnej produkcji przemysłowej.
Części utworzone przez formy są zwykle nazywane “Ordaki” (takie jak stemplowane części, kute części, produkty z tworzywa sztucznego, odlewy, itp.).
Formy i produkty
Ogólnie, Produkcja materiałów opakowaniowych zaczyna się od zamówienia surowców, oraz poprzez współpracę pleśni i sprzętu, Produkty są tworzone. Następnie, Po obróbce powierzchniowej i dekoracji, gotowe produkty są zakończone. Wśród nich, Proces formowania pleśni jest przedmiotem tego procesu.
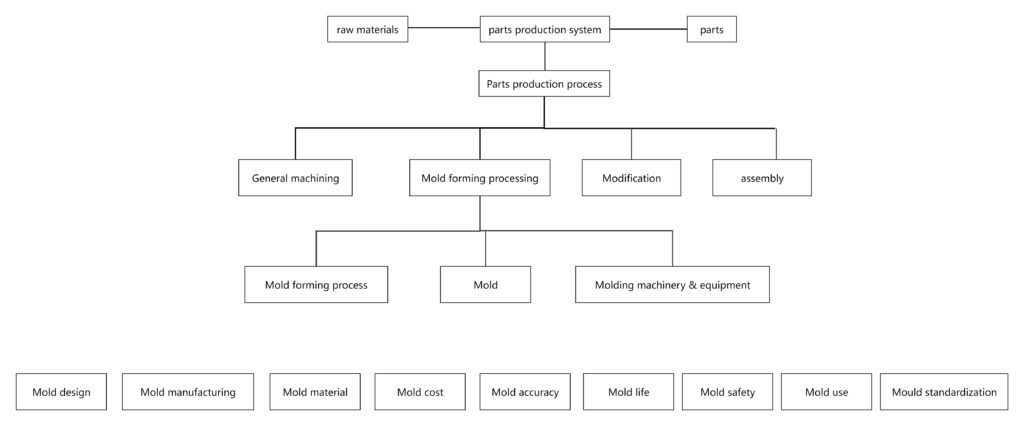
Klasyfikacja pleśni
Formy można klasyfikować na podstawie różnych materiałów produktów, które są używane do produkcji, a materiały samych pleśni są również zróżnicowane. Są one głównie dostosowane zgodnie z produktami. Różne materiały i procesy bezpośrednio określają koszt pleśni.
Zgodnie z tworzonymi materiałami, Formy można podzielić na metalowe formy i formy niemetalne. Metalowe formy można dalej podzielić na formy odlewane (dla nieżelaznych metalowych odlewów i odlewań stalowych) i tworzące formy, itp. Formy niemetalne można podzielić na plastikowe formy i nieorganiczne formy niemetalne. I na podstawie różnych materiałów samych pleśni, Można je klasyfikować jako formy piasku, metalowe formy, Formy próżniowe, Formy woskowe, itp.
Wśród nich, wraz z szybkim rozwojem tworzyw sztucznych cząsteczkowych, Plastikowe formy są ściśle związane z życiem ludzi.
Formy z tworzyw sztucznych można ogólnie klasyfikować jako formy do formowania wtrysku, Formy do formowania, Formy do formowania wspomagane gazem, itp.
Proces produkcji pleśni
Pierwszy, zrobić pleśń, musi być projekt. Musisz wziąć pomysły w myślach i przekształcić je w projekt. Tutaj pojawiają się prototypy. Prototypy przekształcają twoją wyobraźnię w namacalny obiekt. Możesz uczynić to doskonałym zgodnie z swoją wizją. Po zakończeniu prototypu, jest wysyłany do profesjonalnej fabryki form. Fabryka następnie wysyła ją do firmy skanującej, aby zeskanować wymiary. Są to podstawowe dane do tworzenia formy. Tylko przy tych danych można wykonać replikę prototypu. Po zakończeniu skanowania, Do projektowania inżynier projektu formy korzysta z profesjonalnego oprogramowania, takiego jak AutoCAD i Pro/E. W tym samym czasie, Realizowane są również inne zadania, takie jak wybór stalowych pustych miejsc do formy.
Po wybraniu stali, to tylko stos żelaza, a nie forma. Należy go przetworzyć, aby stać się formą. Kiedy stal jest zakupiona, nie można go przetwarzać losowo. Musi być dokładnie przetworzony, i im wyższa precyzja, tym lepiej. Obecnie, Najbardziej zaawansowana technologia może wytwarzać formy z błędem zaledwie kilku mikronów. Jednakże, Takie formy są drogie. Wymagają wysokiej jakości maszyn stalowych i zaawansowanych, które często kosztują ponad milion. Oczywiście, bez wykwalifikowanych pracowników, to wszystko na próżno.
Po drugie, Po wybraniu stali, rozpoczyna się praca. Wykwalifikowani pracownicy przetwarzają każdą część formy zgodnie z rysunkami za pomocą różnych maszyn (takie jak tokarki, płaski, Mierzyny, szlifierki, Elektryczne maszyny rozładowania, Przecięcie drutu, i CNC Centers obróbki). Następnie, Części są montowane i debugowane.
Dla pleśni z prostymi wnękami i rdzeniami, Programator CNC zapisuje program i używa maszyny CNC do przetwarzania formy. Dla obszarów, których nie można przetworzyć przez maszynę CNC, Do przetwarzania używana jest elektryczna maszyna rozładowań. Do form z złożonymi zakrzywionymi powierzchniami, Do przetwarzania używana jest trzyosiowa komputer CNC. Program NC jest generowany na podstawie modelu 3D w Professional Cam Software.
Wreszcie, Po zakończeniu pleśni, jest wysyłany do formowania próbnego. Gdy formowanie próbne się powiedzie, Formę można zwolnić.
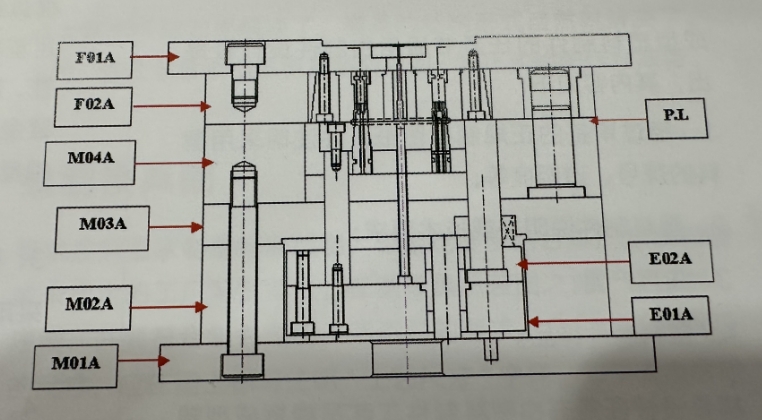
| F01a | Górna płyta mocująca | E02b | Podnośnik rur | E01A | Dolna płyta wyrzucająca |
| F02A | Szablon główny | E02C | Powrót | O02A | Górna płyta wyrzucająca |
| M01A | Dolna płyta mocująca | P01a | Złącze paszowe | F | Master Form |
| M02AAA | Stały talerz | P02a | Lokalizacja pierścienia | M | Męska pleśń |
| M03A | Płyta pomocnicza | P03a | Filar przewodnika | P.L | System rozstania pleśni |
| M04A | Mężczyzna szlifierski | P04a | Rękaw do szpilki |
Zastosowanie pleśni
Formy są szeroko stosowane w branży kosmetycznych materiałów opakowaniowych. Produkty z tworzywa sztucznego, produkty szklane, a wszystkie produkty papierowe wymagają form. Koszt pleśni bezpośrednio określa koszt materiałów opakowania, a także czas dostawy materiałów opakowaniowych. W związku z tym, do materiałów opakowaniowych, Formy są podstawą i fundamentalnymi.









